
Understanding ear infections early, and knowing treatment
options can save you from unnecessary pain — and help protect your hearing and
health.
An ear infection is medically known as otitis media (ASOM /CSOM). It is an infection of the middle ear, a space behind your eardrum.
children are more prone to middle ear infections because of Eustachian tube anatomy and it often clear up on their own.
If you have an ear infection you should visit ENT Specialist to confirm the diagnosis, find the reason behind your ear infection and to get effective treatment.
An ear infection happens when germs — like bacteria, viruses, or fungi — find their way into the ear.
Depending on where the infection is, it may involve:
Infection of the ear canal, often called “swimmer’s ear.”
Infection behind the eardrum, common in children and adults.
Affects balance and hearing. an inner ear infection may actually be a case of inflammation rather than an actual infection
Each type of infection feels different and needs specific care.
Symptoms of Inner ear infection include – dizziness, nausea, vomiting, vertigo and sudden hearing loss
Symptoms of outer ear infection include – pain in the ear, tenderness (pain on touch) redness and swelling of the ear
A middle ear infection is also known as otitis media, acute or chronic suppurative otitis media (ASOM and CSOM). It’s caused by fluid trapped behind the eardrum, which causes the eardrum to bulge. Along with an earache, you may sense fullness in your ear.
Otitis media can come with a fever. You may also have trouble hearing until the infection starts to clear.
If you experience fluid draining from your ear, it could be a sign the middle ear infection has progressed to a tympanic membrane rupture or a hole in the ear drum. This condition can cause a sudden loss of hearing.
A hole in the ear membrane may heal naturally — especially in children below 12 years of age or in adults if it has occurred for the first time. However, in many cases, the perforation may persist and require further evaluation and treatment.
Sometimes, mild ear infections settle down on their own (naturally). But many need timely medical care to prevent complications.
Ear infections can be caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections.
A middle ear infection often starts from a cold or other respiratory problem. The infection moves to one or both ears through the eustachian tubes. These tubes connect back of your nose and throat to behind the ear drum (middle ear area).
An infection can irritate the eustachian tubes and cause them to swell. Swelling can prevent them from draining properly. When fluid inside these tubes can’t drain, it builds up against the eardrum.
An outer ear infection is sometimes called swimmer’s ear. That’s because it often starts as a result of water that remains in the ear after swimming or bathing. The moisture becomes a breeding ground for bacteria.
If your outer ear is scratched by putting your fingers, cotton buds or other objects in your ear, a bacterial or fungal infection can occur.
One of the reasons children are more likely than adults to get ear infections is that their eustachian tubes are smaller and more horizontal than the tubes in most adults.
If you have small eustachian tubes or you have tubes that haven’t developed a slope, you’re at a higher risk for developing an ear infection.
You may also be more likely to get an ear infection if you smoke or are around a lot of secondhand smoke.
Having seasonal allergies or year-round allergies also puts you at risk.
Developing a cold or an upper respiratory infection also increases your risk.
Not every ear pain needs emergency treatment — but certain signs should never be ignored:
Early diagnosis and treatment of ear infection by visiting an ENT Specialist can prevent permanent hearing damage and deeper infections.
A thorough ear check examination is the first step.
At my clinic, I use otoscopy and video oto-endoscopy to closely examine the ear canal and eardrum.
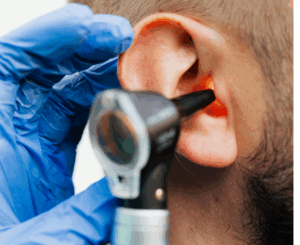 Sometimes, if needed, simple tests like audiometry (hearing test) or tympanometry (middle ear pressure test) may be advised. HRCT Scan of temporal bone may be needed to see the extent of infection or cholesteatoma.
Sometimes, if needed, simple tests like audiometry (hearing test) or tympanometry (middle ear pressure test) may be advised. HRCT Scan of temporal bone may be needed to see the extent of infection or cholesteatoma.
Home remedies may offer temporary relief in ear infection but should never replace proper medical treatment.
Once diagnosed, treatment depends on the type and severity of infection:
Treating Inner Ear Infections:
Rest, medications to control dizziness and inflammation.
Treating outer ear infections
The outer ear should be carefully cleaned. That should be followed by the use of antibiotic or antifungal and anti-inflammatory ear drop.
You may be prescribed antibiotics. Some antibiotics may be taken orally. Others can be applied directly to the site of the infection with ear drops. Medications for pain, such as over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications may also be used to manage your symptoms.
If you’re still experiencing cold or allergy symptoms, you may be advised to take a decongestant, nasal steroid sprays, or an antihistamine.
In most cases, ear infections heal with medicines.
However, surgery may be advised in certain conditions-
Surgical treatments are safe and targeted, done with the aim to ensure safety , protect hearing and improve it.
Healing doesn’t end with medicines or surgery — caring for your ears is just as important.
A little mindful care goes a long way in keeping ear infections away.
To help prevent an ear infection of any kind, follow these tips:
If you suspect you may have an ear infection, it’s important to have it checked out by an ENT doctor.
If an ear infection goes on too long without treatment, it can put an individual at risk of permanent hearing loss and possibly having the infection spread to the brain. However, prompt and proper treatment can usually take care of the infection quickly.
As an ENT specialist in Navi Mumbai, my goal is simple — to help you hear better, feel better, and live fully.
If you or your loved ones are facing recurring ear issues, don’t wait for the whispers to turn into alarms. Visit an ENT Specialist.
Read about common causes of ear pain in & How ENT specialists diagnose ear pain my previous blog post. Stay tuned.
Common signs of ear infection include ear pain, a feeling of fullness, reduced hearing, fluid discharge, and sometimes fever. If symptoms persist, it’s best to consult an ENT specialist.
Mild ear infections, especially viral ones, can sometimes resolve without treatment. However, if symptoms worsen or don’t improve in 2–3 days, Ear check up by an ENT Specialist is necessary.
Clearing an infected ear safely requires medical advice. Avoid inserting cotton ear buds, q-tips or other objects into your ear. Treatment may include thorough cleaning of pus in the ear by ENT, antibiotic drops, oral medications, or minor procedures guided by your ENT doctor
To prevent infections, keep your ears dry after swimming or bathing, avoid inserting foreign objects, and maintain good ear hygiene. If you’re prone to infections, consult an ENT doctor for preventive care.
Some mild ear infections can improve within 2–3 days without antibiotics. But bacterial infections often need treatment and may take up to a week or longer to fully heal.
Read my next blog about common causes of ear pain.

Hi, I’m Dr. Archana Jhawar, an ENT specialist with over 24 years of experience. I specialize in tinnitus treatment, vertigo , ear care, and ear surgeries, practicing at Neoalta Clinic, Vashi, and Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital in Navi Mumbai. I’ve trained in vertigo management and Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT), combining science with compassion to offer holistic, evidence-based care. I’m passionate about writing, poetry, music, yoga, and photography.

